7.2.Schedules
(Email Archive ⇒ Settings ⇒ Schedules button;
File Archive ⇒ Settings ⇒ Schedules button;
SharePoint Archive ⇒ Settings ⇒ Schedules button;
Custom plugins ⇒ General ⇒ Schedules button)
How to use schedulers in contentACCESS?
Jobs in contentACCESS can be automatically triggered with the help of schedules. Schedules are used to define, when a processing task should start automatically and when the processing should end and restart again. In other words, administrator may schedule jobs which will automatically run at times, which are configured in the given job’s scheduler settings. It is possible to set numberless schedulers and then select the appropriate one when configuring an exact job. Schedules help the users to work more efficiently, so they won’t have to waste their time by logging into the software and starting the processing manually.
Navigate to the Schedules page from the  Schedules button on the ribbon. Here click on + new option. In the Add new scheduler dialog window enter the scheduler Name, select the Type of scheduler from the dropdown list. In contentACCESS, there are 3 types of schedulers which can be set: One time, Always run and Week schedule with repeat.
Schedules button on the ribbon. Here click on + new option. In the Add new scheduler dialog window enter the scheduler Name, select the Type of scheduler from the dropdown list. In contentACCESS, there are 3 types of schedulers which can be set: One time, Always run and Week schedule with repeat.
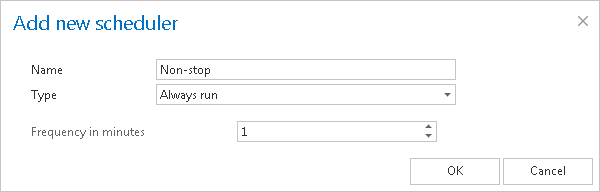
One time will run only once; by this type of scheduler we specify the start date only; the job will end when it finished the processing. One time schedulers are often used by restore or recovery jobs, i.e. by jobs which are run occasionally. The schedule that we set up now will start to run on 7th of September at 6 PM, and will end once the job finished its task:

Week schedule with repeat
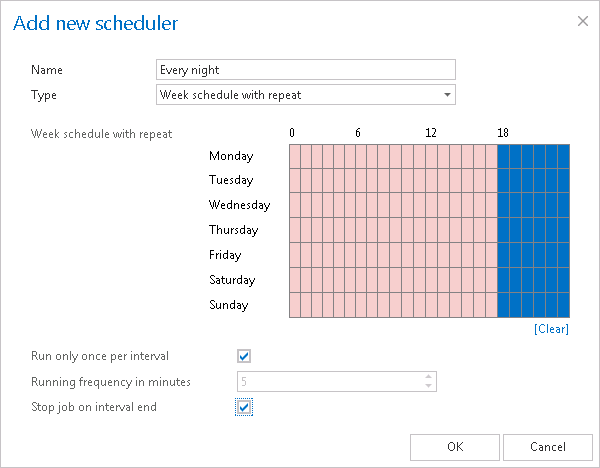
will run at the same hours every week, repeatedly. In the scheduling tab click on the fields to set the days and hours, when the processing should start. One cell represents one hour. By using the Running frequency in minutes option the user may set the time intervals, when the scheduler should check if the job is running. If running frequency is set e.g. to 5 minutes, then the scheduler will check in every 5 minutes, if the job is still running. If it is running, then it will check the running after 5 minutes again: if it is not running, then the job will be started again. It is worth to use this option if the processing should run continuously, e.g. from morning to evening, and if new tasks for processing are added continuously. If we check the Run only once per interval checkbox, then the running frequency will be automatically deactivated and the job will run only once during this time period. It is recommended to run a process once in an interval, if the processing should be performed e.g. at the end of each working day. With checking the Stop job at interval end checkbox the user may stop a job after the set time interval. You don’t have to mind any unfinished processing, the job will be forcibly stopped and started again, according to the scheduler settings. The red color of the Add new scheduler’s cells mark the time intervals, when the job is not running.Our “Every night” scheduler (its setting can be viewed on the screenshot below) will run the job from 7 PM till midnight, will stop processing at midnight, even if the process is not finished. It will run only once during this interval. We can use a similar scheduler to archive the old company documents. It makes no sense to select running frequency in this case, because during the night nobody will add new files to archive into the file location.
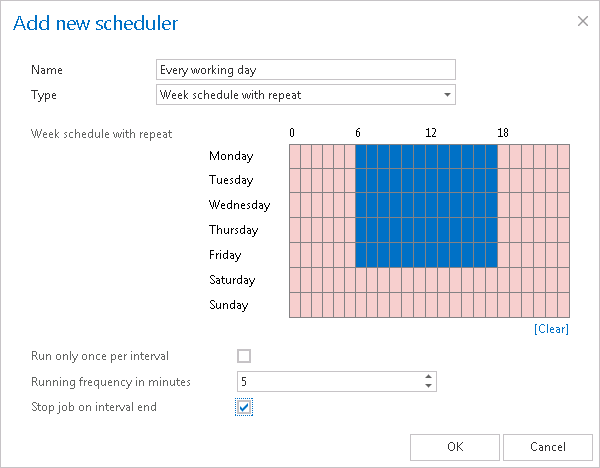
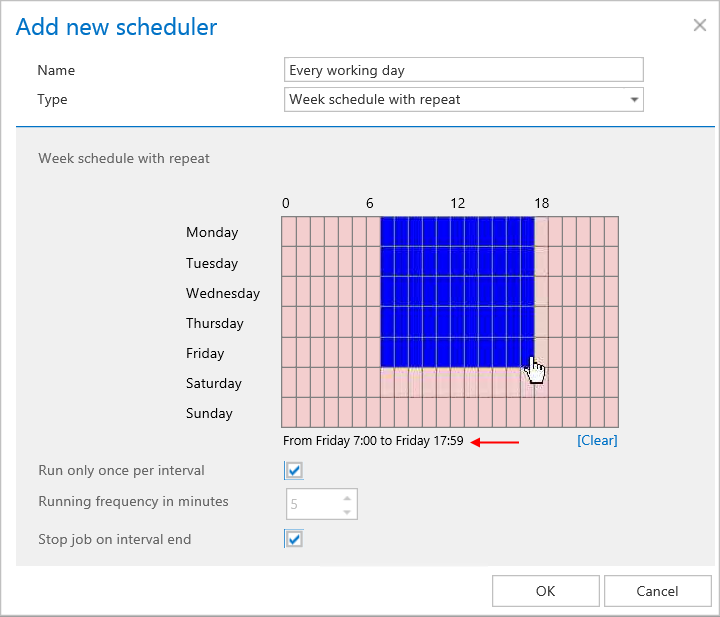
Setting the Running frequency in minutes option might be useful when the user is archiving from an Exchange journal mailbox for example, or from any location, where the tasks to be performed are accumulating continuously during a time period. If the job has processed all the items, the schedule should be also periodically checking if there is anything new to archive. The “Every working day” scheduler (on the screenshot below) is set to process the email records from 7 AM till 6 PM. The first archive process will run from 7 AM until it has finished all current tasks, and the scheduler will check each 5 minutes if any new tasks (email records) were added to process. The archiving will end at 6 PM each day, even if there is something left unfinished. A scheduler similar to this may be set to archive journal mailboxes on the Exchange:
This scheduler type is often used to run provisioning jobs, too.
If the user would not like to end the processing at 7 PM, he should uncheck the “Stop job at interval end” option.
Tip: When the user is setting a desired time range or just moves the cursor over the selected time range, the Weekmap scheduler highlights this time range and displays the exact start and end times beneath the calendar:
It is possible to edit or delete a scheduler’s configuration using its context menu (left click on  next to its name) if any modifications must be implemented. The scheduler type and its description can be also viewed in the grid.
next to its name) if any modifications must be implemented. The scheduler type and its description can be also viewed in the grid.
The “manage access” option allows to grant access permissions on the selected scheduler for a second user. This “manage access” option is available for the logged on administrator if his role assignment contains the Edit scheduler – All allowed permission on the tenant. Read more in Managing access to contentACCESS objects.
