- Introduction to contentACCESS
- contentACCESS setup package
- contentACCESS components
- contentACCESS Tools
- Tenants in contentACCESS
- General system configurations
- Connection
- User interface
- Users in contentACCESS
- Invitations
- Roles
- Login providers
- System
- Licensing
- Notifications
- Monitoring — how to find out possible misconfigurations / reasons of potential system/job failures
- Auditing
- Distributed environment in contentACCESS — Clusters
- Statistics
- Legal hold
- Task runner
- Indexing
- SMTP Servers
- SMTP Mappings
- How to create/configure databases — All databases
- Common features
- Creating new jobs in contentACCESS
- Jobs’ page, jobs’ context menu
- Filtering in jobs
- File Archive
- Introduction to File system archive
- File archive settings
- File archive Databases
- File archive System settings
- File archive Retentions
- File archive Storages
- Root folders
- Aliases
- File archive Schedules
- Provisioning settings and managing access to contentWEB
- Remote agents (file archive)
- Global rules (remote file archive)
- Configuring aliases
- Configuration of jobs available in contentACCESS File Archive
- Configuration of File system archive job
- Configuration of a File system restore job
- Configuration of File system recovery job
- Configuration of Delete job in File archive
- Configuration of File system shortcut synchronization job
- Configuration of Remote shortcutting job
- Active/inactive documents in File system archive
- Email Archive
- Important settings before creating an Email Archive job
- Database settings
- Email archive System settings
- Email archive Provisioning settings
- Retention settings
- Shortcuts in email archiving
- Storing of archived emails
- Creating email archive schedulers
- User experience
- Address book objects
- Granting access rights for mailbox users and explicit users to view the mailbox archive
- Database and store assignment in email archiving
- Mail app access
- Remote agents (email archive)
- PST import
- Creating Email archive jobs: archive, restore, recovery, delete, mailbox move, shortcut synchronizaion, shortcut repair
- Email archive job
- Email restore job
- Email recovery job
- Configuration of Delete job in Email archive
- Journal post processing job
- Mailbox move job
- Shortcut synchronization job
- Shortcut repair job
- Public folder archiving
- SMTP archiving
- SharePoint archive plugin
- GDPR plugin
- Custom plugins
- ThreatTest
- officeGATE
- contentACCESS Mobile
- Virtual drive configurations
- Application settings
- Terms of use
- FAQ
- Download sample for the file to be imported does not work
- Archiving is not working if MAPI is set to communicate with the Exchange server
- Virtual drive is still appearing after the uninstall
- Outlook forms problems
- Unable to open shortcuts of archived files on the server side
- Samples are not shown using 'Show sample" option in the Import dialog
- Do I need to create separate tenants for file archiving and email archiving
- What is the recommended database size for email, file and Sharepoint archiving
- The TEMP folder is running out of space when archiving big files
- The attachment could not be opened
- After updating Exchange 2013, the EWS connection might not work in contentACCESS
- If Windows authentication is not working in contentACCESS and an alias was created for contentACCESS
- contentACCESS Outlook add-in certificate issue
- PowerShell scripts for setting up Email archive
- Solution for Outlook security patches
- Solution for Outlook security patches through GPO
- Solution for indexing PDF files
- O365 SuperUser mailbox configuration
- Office365 journaling
- Organizational forms
- Multifactor authentication
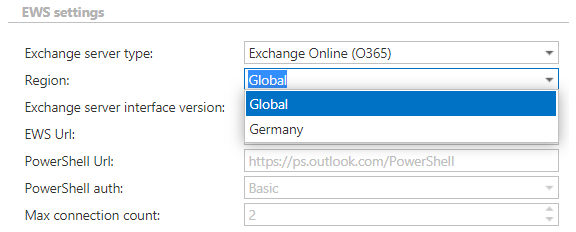
- Region setting
22.22.Region setting ↑ Back to Top
Microsoft Azure is hosting multiple instances of the Azure cloud services, which are isolated from each other. The most commonly used Azure instance is the Azure Public Cloud. This Public Cloud has several data centers around the world. The data hosted in the Public Cloud are replicated/stored in these data centers. However, some government regulations in some countries have special requirements. Microsoft has deployed isolated Azure instances for such scenarios. One of these isolated instances is the so called German cloud, which is hosted by the Deutsche Telecom in Germany. Another isolated instance of Azure is the Government Cloud, which is hosted in USA.
The Region setting is used to specify in which Azure instance is the current tenant located. Choose:
- Global – if your tenant is hosted in the Azure Public instance
- Germany – if your tenant is hosted in the German Cloud (hosted by Deutsche Telecom)