7.4.1.Amazon S3
Introduction to Amazon S3 Storage
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a cloud-based storage solution by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows you to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web. It is highly scalable, durable, and cost-effective, making it ideal for a variety of use cases like backups, archiving, content delivery, and data analytics.
S3 organizes data into buckets, which act like folders, and stores individual files as objects identified by unique keys. It supports flexible storage classes for different needs, from frequently accessed data (S3 Standard) to long-term archiving (S3 Glacier). S3 is also highly secure, offering encryption, access controls, and integration with other AWS services.
Key features include its pay-as-you-go pricing, and ease of integration with tools and services. It’s used for tasks like hosting static websites, streaming media, and providing storage for applications. Whether you need high-speed access or affordable archival storage, Amazon S3 adapts to your needs, ensuring reliable and secure data management.
How to configure the Amazon S3 Storage
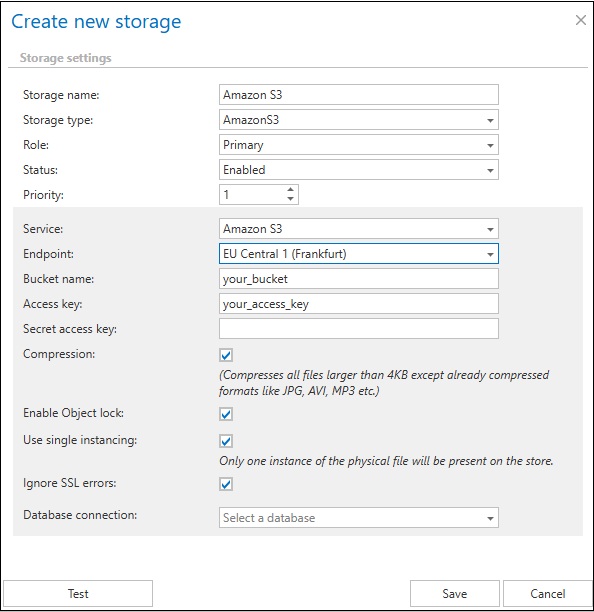
First, you set the Storage name, the Type (Amazon S3), the Role (None or Primary), the Status (Enabled, Disabled, Unavailable, Removed), and the Priority. For more information about Roles and Statuses, please refer to this chapter of the documentation.
Once the storage type (Amazon S3) is selected and the Role and Status is set, you will be able to choose Amazon S3 from the service dropdown menu.
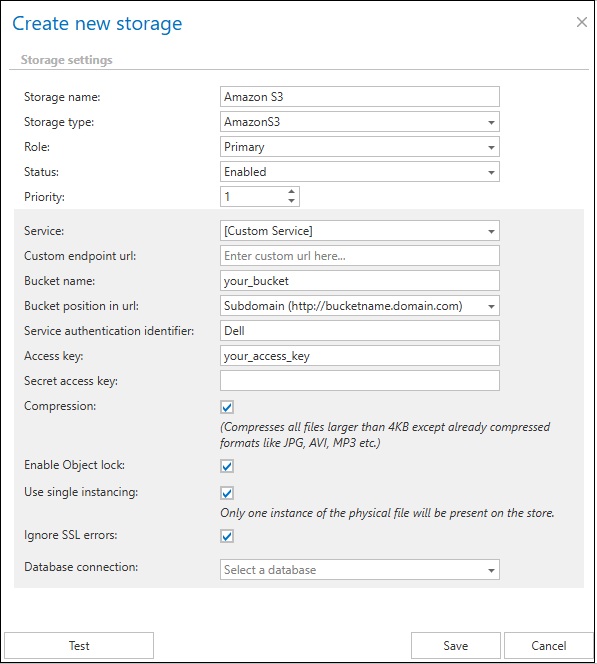
The store connects to the endpoint that you select for a specific service. In contentACCESS, the service endpoints for Amazon Simple Storage Service and Alibaba Cloud Object Storage, which also uses Amazon S3 interface, are preconfigured. If you want to use a different cloud service, which supports Amazon S3 interface, it is possible to select Custom service URL for the service and then enter a custom URL for that service endpoint.
Configure the bucket used to store objects in Amazon S3 by entering its name in the Bucket name field. Ensure that the bucket already exists in your AWS account and that it is located in the selected region.
The Access Key and Secret Access Key are used to authenticate the caller by the cloud service. These keys are provided by the cloud storage service.
This store type also supports:
- Compression – all files larger than 4 kilobytes will be compressed, except for already compressed file formats such as JPG, MP3, etc.
- Enable Object lock – S3 Object Lock is a bucket-level setting that, once enabled, allows you to make objects immutable. You cannot use Object Lock features, such as setting retention periods or legal holds on individual objects, unless Object Lock is first enabled on the bucket itself. Please note, that enabling Object Lock is a permanent action for a bucket. Once enabled, it cannot be disabled. When this option is enabled, contentACCESS verifies whether Object Lock is enabled on the target S3 bucket and throws an error if it is not. Retention settings are written to the bucket objects only if this checkbox is selected. In environments using single instancing, the longer retention period is always applied or preserved across all instances. The retention changer function also works correctly in this mode, which is why Governance Object Lock is used in this setup.
- Use single instancing – it will keep only one copy of the physical file in the store
- Ignore SSL errors – the system will bypass and not validate SSL/TLS certificate errors